The question “How much does an app cost?” isn’t an easy one to answer. There are lots of variables, and everything from the set of features you want to the layout of your user interface comes into play. That’s without even touching on the native vs. hybrid debate!
In this article, mobile app development experts from Iflexion are going to look at some of the main factors that can determine the end price of an app, along with reviewing some of the main sources of information from around the web. One of the problems with providing a catch-all set of quotes for different types of apps is that things change quickly. So, our aim is to provide a comprehensive answer that’s based on data and industry knowledge. Let’s dive in.
Consideration 1: Development Time
It can be argued that everything ultimately comes down to development time. There can be drastic differences in cost depending on whether you pick a freelancer, an outsourced team or a high-end boutique agency.
Freelancer Development Hours by App type for (1) Apple and (2) Android

Image Source: Upwork
Reputable agencies often offer much more than independent developers and cut-price firms. Native development demands a high level of engagement with frameworks, SDKs, platform hardware and industry trends and benchmarks. Well-defined processes that have been tweaked over dozens or hundreds of successful projects and that conform to up-to-date best practices are rarely found at the lower end of the price scale.
The more complex your app, the greater the need for these processes becomes. Freelancer rates can be ideal for a simpler app, where the potential for issues is smaller. Enterprise apps, however, will benefit from a reliable, trusted firm with a foolproof approach.
Consideration 2: Features
There are a few points to mention in regard to features. For app-centric business, where revenue is significantly or exclusively dependent on in-app subscriptions, purchases or advertising, the set of necessary features can be extensive and unique, both of which will impact the final price.
The app market, which has more than doubled since 2014, is continuing to grow. And the demand for more efficient, intuitive and innovative features has likewise become more pressing. Feedback mechanisms, user-facing customizability and simple in-app purchase options all illustrate this trend.
Worldwide Mobile App Revenues in 2015, 2016 and 2020 (in billion U.S. dollars)
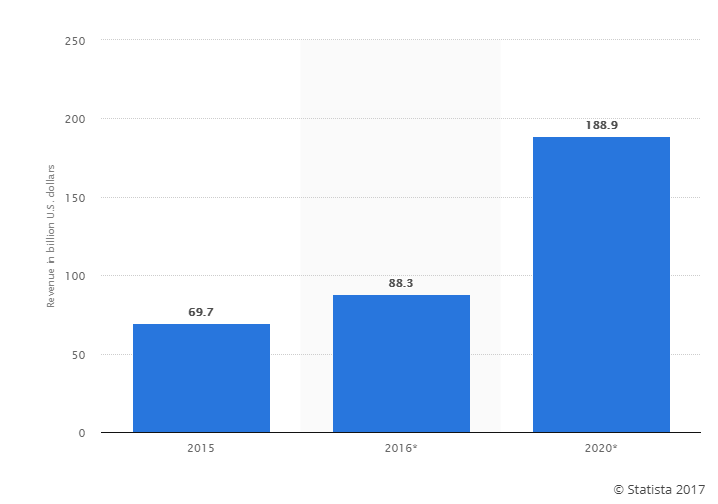
Source: Statista
It’s worth pointing out, however, that many businesses don’t need a feature-rich app that’s going to act as the focal point of their customer-facing activities. If you’re Uber, then your app is obviously foundational. But for most retail and service-based companies, an app is a secondary consideration meant to streamline certain aspects of their existing customer journey, like loyalty schemes and promotional updates.
There is a range of frameworks and out-of-the-box services catering for this kind of demand. Very often, building an app for a loyalty program or online store can be a case of customizing the layout and branding in a third-party app builder. You can then let them handle the rest. Hybrid PHP frameworks like Laravel and Symfony allow for greater functionality while significantly reducing development time and thus cost.
Consideration 3: Complexity
Remember to evaluate complexity in the context of your business needs. What problems are you trying to solve? Because there is a direct link between app complexity and cost, it’s worth outlining the basic functionalities that you need in order to deliver your intended features, cutting off the unnecessary fat as you go.
Do you, for example, need a dedicated back-end server? If you need your app to interface with its own server, as an increasing number do these days, then expect the cost to rise significantly. A host of backend cloud services such as Parse and Kinvey make this process much easier, but development time can still add up. Most companies take it for granted that their app will be able to deal with storage, analytics, scheduled notifications, online stores, customer data, etc. But it’s important to remember that all of these functions have a significant server-side element, and things can get complex quickly.
Estimated Cost to Develop Popular Apps
- Twitter: $50,000;
- Whatsapp: $250,000;
- Uber: $1,000,000;
- Pinterest: $120,000;
- Angry Birds: $2,200,000.
Source: NextWeb
Different agencies, bloggers and news platforms, however, are surprisingly consistent in their estimates for a simple app. Have a look at the quotes from a handful of key sources below.
While features are user-facing capabilities of your app, the complexity is the behind-the-scenes functionality required to deliver them. Many companies find that their costs can significantly be reduced by simplifying certain features, thus lowering the back-end complexity while still effectively solving their customers’ problems.
Consideration 4: Platform
A normal industry practice is to start with an iOS app and develop for Android and Windows at a later stage, given the differences in development complexity (it’s harder to code for Android than iOS).
Opting for iOS first, and developing for Android later, can be a chance to gather user feedback and work through any bugs. Smaller businesses can often afford this freedom without any major drawbacks, and this can offer a useful window into the development process.
Consideration 5: Budgeting beyond development
A lot of developers point out that it’s important to view the process of building an app in the context of a broader business plan. While there will be related yet somewhat separate costs such as marketing and sales, there are other processes that tie in directly with an app’s performance. The cost of regular updates and bug fixes, for example, can add up. Customer support is another key area. Maintenance of the technical side of back-end sales related to in-app purchases and subscriptions is also vitally important. These are all things to think about.
Conclusion
How important it is for you to have an app fundamentally depends on your type of business. For large enterprises, not having an accessible app through which to communicate with and sell to customers becomes a significant competitive disadvantage. For a smaller business, a branded app can be beneficial in a lot of areas, particularly customer loyalty and promotion, although it’s certainly not a case of make-or-break.
Whatever your business, and whether you choose to work with an agency, freelancer, or run your own in-house team, it’s important to think about your potential app’s features and complexity in the context of your own specific goals. Maintaining this broad approach will allow you to minimize the costs and development time in the long term.



Comments
0 comments