With Android being the most popular mobile operating system and Java being the language of the Android OS, you have no choice but to take advantage of Java to build portable applications for mobile devices. Although you can code a mobile app without Java, by using Java and the Android SDK (Software Development Kit), developers can create faster and more reliable apps. Likewise, tools for development of Java apps for all other operating systems apart from Android are also available: you are free to develop apps for iOS, Windows, and other less popular OSs.
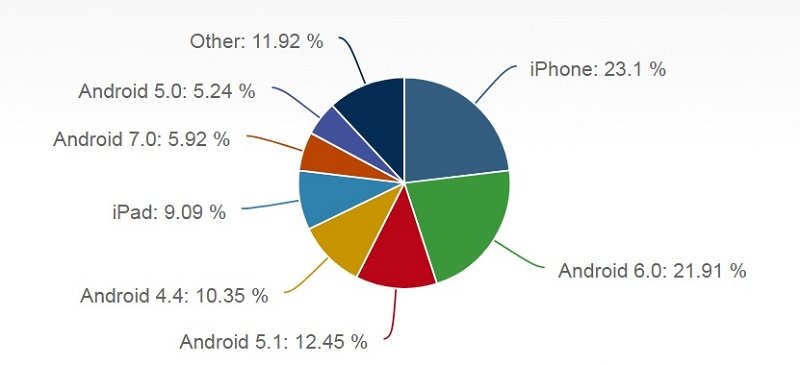
Source: NetMarketShare
Why Choose Java?
Java Virtual Machine, or JVM, is a tool that allows a program’s code to run on any device – desktop, mobile, or a home appliance, for instance. With Java, you can embed code in literally any device, using the concept of “write once, run everywhere.” That is why, Java is one of the leading languages used for mobile development: devices manufactured by different companies may differ a lot regarding hardware and firmware, and you need an option to run your app on a variety of them.
Mobile Java apps run in a sandbox environment where the actions performed by the app cannot harm the underlying operating system or other applications. Well, no code is 100% secure, but sandboxing is a viable method to isolate an app and run it in a controlled environment, which is necessary when privacy and security are concerned.
Most mobile sites and apps using Java utilize Java SE (Java Standard Edition) and Java ME (Java Micro Edition), which have all the features and capabilities for developing apps for mobile and embedded devices. This means that you can develop software for most tablets and smartphones on the market just using this language.
Portability is another key feature behind Java’s popularity on mobile devices. By writing a code in Java, a software developer can take advantage of the native capabilities of the device, eliminating constraints such as low memory or display limitations. Furthermore, Java code reduces battery drain, while battery life is a major feature of any reliable mobile device.
Using Java for Cross-platform Development
A good number of businesses need their mobile app to run both on iOS and Android. It is also common for a mobile app to have a web version, thus covering all possible online use cases. You can develop a native app for Android using Java, but you will need an emulator for Mac. Fortunately, lots of tools are available to customers and developers who need an app running under any OS and on any device.
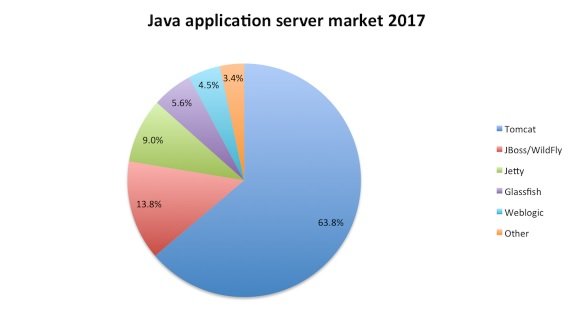
Source: Plumbr
Java not only runs on all mobile platforms, but it also suits for a variety of uses, including server apps, big data, embedded space, and games. By being platform-agnostic, Java is among the primary contenders for the leading cross-development language. In addition, you can integrate Java programs using APIs while benefiting from numerous available open-source libraries.
Currently, developers can use Java Development Kit versions 6 to 8, with Java 7 and Java 8 dominating the market. There are a few notable differences between Java 7 and Java 8, but both versions provide all the features required to build a mobile app.
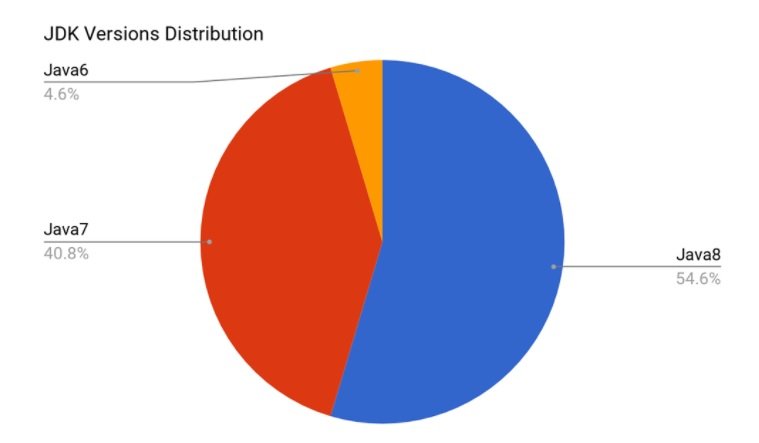
Source: DZone
Bearing in mind that Android is powering some 60% of all mobile devices in the world and adding that Android’s Java version is quite similar to the standard Java, you can barely avoid this programming language when creating mobile and web apps. Eclipse and Android Studio are the most popular IDEs (Integrated Development Environment) for the development of Java apps with Google recommending the use of Android Studio.
Java Mobile Development Challenges
Apparently, you can easily find all the tools you need to build a mobile Java app. The challenges of mobile Java development have to do mostly with integrating a growing number of cloud services, as well as legacy applications using custom or off-the-shelf APIs.
Other challenges are related to the development of apps for platforms that do not provide native support for Java and Android OS. About the half of the global mobile market (40%) that does not belong to Android is the market share you should not take lightly, especially when industrial devices are concerned. The growing Internet of Things market poses further challenges where you have to deal with a variety of devices running different firmware and where security is still a massive issue. That is why most medium and large businesses select to outsource complex Java projects to Java development company Itransition or another reliable developer.
Most Java apps now run in the context of mobile use and must connect to a third-party service, such as social media and productivity software. Integrating a Java app is easy, but you still need to provide the required level of security, especially when creating enterprise applications. You can use the Java Embedded Suite to introduce middleware capabilities and web-interfaces for managing devices, but you must also secure the device communications, inputs and outputs, and provide reliable data storage.
We also have Java Card, which provides developers with a secure environment to build apps running on very small devices or smart cards. You can run multiple apps using the latter and add further applications after issuing the card, but Java cards should have additional security layers since they are mostly used for various transaction and data exchange applications.
Nonetheless, Java is the most widespread language for mobile app development and is set to retain its leading position in the near future.




Comments
0 comments